
Environmental protection at Hamburg
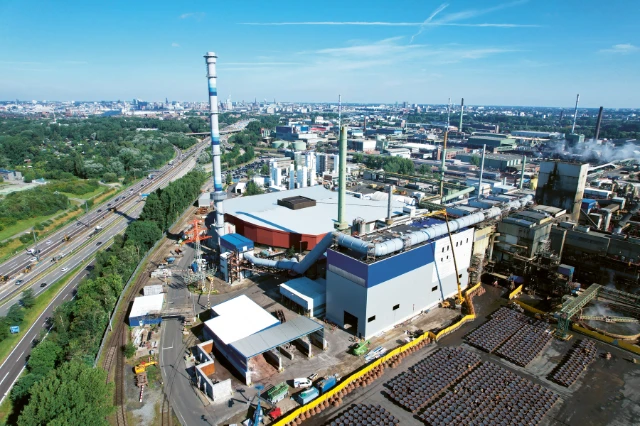
The largest Aurubis AG production site and the Group headquarters are located on the Elbe island Peute, only about four kilometers, as the crow flies, from Hamburg’s city hall. The site covers an area of 870,000 m².
Aurubis AG’s Hamburg site is one of the world’s state-of-the-art primary and secondary copper smelters. It produces around 400,000 t of pure copper from copper ores, recycling materials such as scrap, and other various complex recyclable materials. Multimetal recovery also generates other metals, such as precious metals, nickel, lead and zinc, as well as iron silicate products and sulfuric acid.
Metal production in the middle of a large city isn’t simple, but Aurubis is committed to ensuring environmentally sound copper and multimetal production in this challenging setting. This requires dedication that goes beyond the legal stipulations. After all, protecting the environment and the health of our neighbors and employees is the foundation of a sustainable business. We need to, and we want to, combine the city’s growth targets with the sustainable development of the Aurubis site in Hamburg. With the support of our employees’ environmental awareness, we attain exemplary achievements in environmental protection and work on continuous improvement using innovative, high-performance technology.
The Environmental Protection department at the Hamburg site is responsible for implementing and monitoring all the applicable environmental requirements. These include the relevant laws, e.g., the German Federal Immission Control Act (BImSchG), the Recycling Management Law (KrWG), and the Water Control Act (WHG); stipulations in plant permits; Group requirements; and voluntary agreements regarding improvement measures, such as the Partnership for Air Quality and Low-Emission Mobility.
We use an environmental management system as an instrument to monitor legally compliant operation and to support continuous improvement. This system is monitored annually and certified every three years pursuant to DIN ISO 14001 and EMAS by an accredited body. The environmental management system has been part of an overarching integrated management system (IMS) since 2017, which still includes the quality (DIN ISO 9001), energy (DIN ISO 50001), and occupational safety (DIN ISO 45001) management systems.
To ensure that facilities are operated pursuant to the relevant laws, extensive measurements are carried out in the scope of environmental monitoring in accordance with the applicable technical standards. The high measurement density means up to 10,000 individual analyses are carried out for air and 7,000 for water. Noise and vibration measurements are also taken. Automated measurement procedures play an important role in this process and further increase the data density in environmental monitoring, enabling the best possible precautions.
Routine inspections and audits take place in the production areas to ensure they are operating correctly. Every year, around 1,000 employees complete training to boost their understanding and awareness of environmental issues in everyday work. Modern digital learning methods increase learning efficiency. The management of the production divisions is kept up to date on new legal developments relating to the environment in separate informational events.
Preventing fugitive dust emissions and water pollution control were identified as the most important environmental aspects at the Hamburg site. Other key topics include avoiding waste, raising the recycling rate, and supporting biodiversity and low-emission mobility. Improvement measures are derived and implemented based on the significance of these environmental aspects.
You can find detailed environmental information for the Hamburg site in the current Environmental Statement. (German only, english version to follow)
Environmental Protection - facts & figures
While considerable improvements were made by installing filters in the chimneys in the early 1990s, additional improvements are more difficult to achieve these days. Nevertheless, fugitive dust emissions will be reduced by using newly developed filter media and suctioning off and filtering dust from roof openings in the future.
Since 2000, dust emissions at the site have been reduced, both specific (-56 g/t of copper output per year) and absolute (-32 t per year). The voluntary emission reduction agreements entered into with the city of Hamburg have always been fulfilled.
Our plants already operate using the best available off-gas cleaning techniques. But a low level of emissions remains, mainly influenced by fugitive emissions. In many cases, appropriate reduction systems are not proven or available on the market with the required efficiency. Despite these challenges, Aurubis plans to continue further reducing especially fugitive dust emissions in the future with tailor-made solutions, for example efficient and demand-controlled suctioning and filtering of building ventilation air at roof openings or utilizing newly developed filter media.
We will invest € 100 million in measures to further reduce emissions in the primary smelter at the Hamburg site. These measures include optimized source extraction, a newly installed procedure for processing intermediates, and the use of state-of-the-art suctioning and filter technology to trap residual dust emissions. After our plans are fully implemented, we will reduce fugitive emissions from the primary smelter by 80 %. All of this contributes to our sustainability strategy and makes the location fit for the future in the long term.
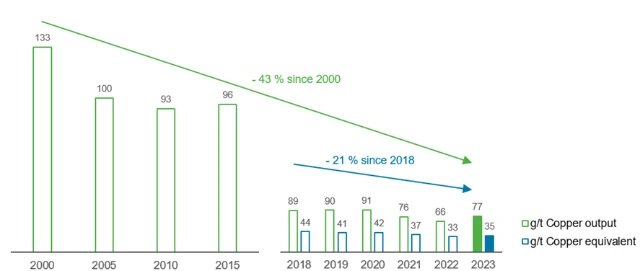
Dust emissions g/t of copper output and in g/t of copper equivalent
Due to optimizations in the plant’s internal sewage treatment facility, metal emissions to water have decreased by about 35 % per ton of copper output and by approximately 40 % in absolute terms since 2000, taking into account the normal range of fluctuation. Additional improvements are planned, such as increasing dwell times and enhancing precipitation of the metals.
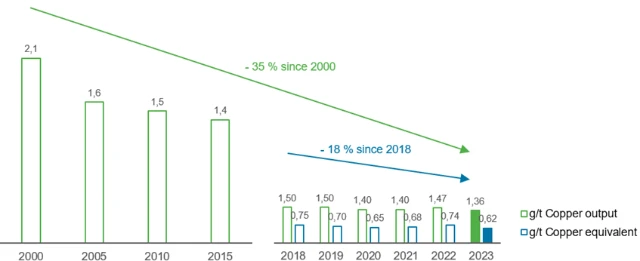
Metal emissions in g/t of copper output and in g/t of copper equivalent
By using raw materials and energy sparingly, we are acting responsibly towards future generations. From a long-term perspective, the specific energy consumption at the Hamburg production site has been significantly reduced in recent decades, by 45 % compared to 1990.
The more measures that have been implemented in energy efficiency in the past, the more challenging further optimization is. Moreover, because there are technological limits to reducing energy consumption and emissions, the improvements being achieved today within the plant boundaries are only marginal compared to previous years. This is despite the same or higher levels of investment, which were already high to begin with. For example, complex recycling raw materials with relatively low metal contents and complex ore concentrates require more energy to be processed. As a result, we focus not only on further increasing efficiency but also on solutions that save energy and thus prevent CO2 outside of our plant — such as the Industrial Heat project in Hamburg with a total reduction potential of up to 140,000 t CO2/a. Furthermore, we are increasingly considering measures to replace fossil fuels with alternatives, for example by commissioning the 10 MW power-to-steam plant. Assuming that 100 % of the power supply comes from renewable energies, this plant alone could cut about 4,000 t of CO2 annually. The reduction of greenhouse gas emissions is taking a higher priority in investment decisions as well.
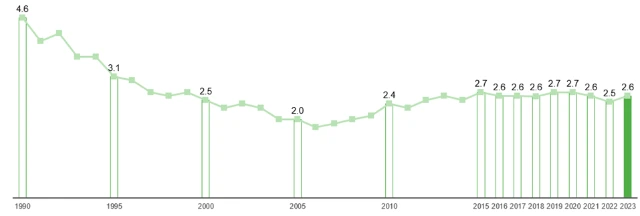
Energy consumption at the Hamburg site in MWh/t of copper output
Environmental Protection Measures & Projects
Reducing Diffuse Emissions (RDE) in primary copper production
- All measures can reduce diffuse emissions from primary copper production by 80 % when fully implemented. The first phase has been successfully implemented. The second phase is in the preparation stage.
- Gradual completion 2020–2025
Further reducing fugitive emissions in secondary copper production
- Optimizing phase separation and reducing exposed bulk stocks
- Completed by the end of 2023
1. Further extracting industrial and non-fossil fuel waste heat, up to an additional 38 MW from sulfuric acid production lines 2 and 3 and feeding it into the existing urban transmission grid.
- This second stage of the Industrial Heat project started in 2018 can additionally save more than 100,000 t/a of CO2
- Implemented in 2024
2. Reducing CO2 emissions through various measures:
- Reducing natural gas in the anode casting machine and channel area and at the center lance of the flash smelter furnace.
- Installing more efficient pumps and fans, mainly with rotation speed control
- Reducing compressed air losses in secondary copper production, new construction of efficient compressed air generation systems
- Replacing limestone with blast furnace slag as an additive in secondary copper production
- Installing new anode furnaces specially designed for the future use of hydrogen as a reducing agent (saving 6,000 t of CO2 per year)
- Installation of LED lights
- Implemented in 2023 and 2024
- Further reducing the amount of wastewater in acid production
- In addition to the already implemented reduction of the cooling water demand through the extraction of industrial heat, a further optimization of the cooling processes is planned. In the process, the discharge volume of the existing cooling towers is to be reduced by 500,000 m³/a, fulfilling the necessary conditioning requirement of the cooling circuits.
Commissioning in 2024
2. Reducing metal emissions
- Reducing metal loads by various optimizations in control systems
Implemented in 2023
In our eyes there is no contradiction between nature conservation and industrial production. Wherever possible, we endeavor to support the necessary further development of the plant as well as the promotion of urban biodiversity.
Together with the environmental authority and NABU, measures were also agreed in 2024 as part of the UnternehmensNatur network to help protect nature and species in Hamburg.
As part of a survey, further measures to promote urban biodiversity were coordinated, with a focus on reconciling the goals of promoting urban diversity with the projects for plant development and transformation.



Certain open spaces on the site offer opportunities to develop habitats, particularly for insects and birds. Supplementary greening of the edges and shoulders of roadways with native plants can increase biodiversity. Where possible, sunny areas are made into wildflower areas and maintained with appropriate extensive care. These are important biotopes for insects such as wild bees, bumblebees, hoverflies and butterflies.
Vertical planting and green roofs remain important options for optimizing the use of limited space.
Maintaining the peregrine falcon territory at our plant remains a priority. In 2024, we were pleased to welcome three young birds.
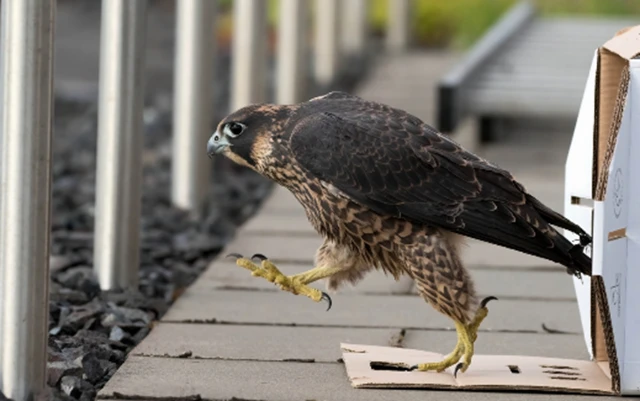

Peregrine falcon released after brief veterinary treatment following an accident
Environmental Protection milestones at Hamburg site
Further technical modifications to the contact plant’s acid coolers in line II and III. Investments of around € 100 million. The utilization of 40 MW of waste heat means a CO2-free district heating supply to heat up to 20,000 Hamburg households and a CO2 savings of approx. 100,000 t/a. The project thus significantly increases the site's energy efficiency and makes a major contribution to the climate protection goals of the city of Hamburg.

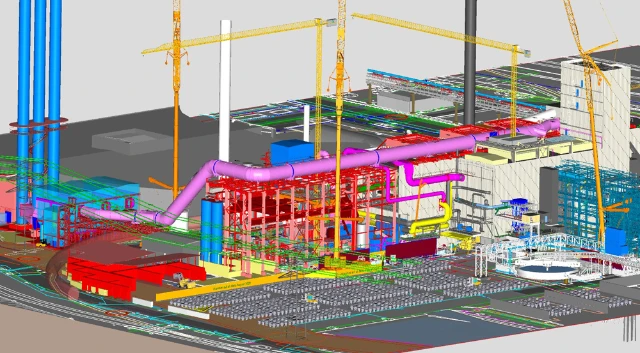

Step-by-step implementation of measures to further reduce fugitive dust emissions from primary copper production. The project includes efficiency improvements in existing capture systems close to the source, aided by measures to optimize the hall circulation conditions. An additional part is the installation of new aggregates for the low-emission treatment of internal intermediate products. In addition, the gradual installation of a purely demand-driven collection and cleaning system for residual fugitive emissions at the roof is an important part of the innovative design. The roof suction is designed to be extended in steps. A high level of energy efficiency is achieved through the control concept, which is adapted to the actual demand at any given time. The overall measure is expected to reduce fugitive emissions from primary copper production by about 80 %, which would result in an exemplary, clean operation even on a global scale. The project started in 2020. Gradual implementation, first step to be completed in 2022. Investment: € 100 million. The second phase is in the preparation stage.

Commissioning of a steam turbine to generate electricity. The previously unused pressure stage between 60 and 20 bar is made usable with the help of a superheater. This reduces about 5,000 t of CO2 per year.
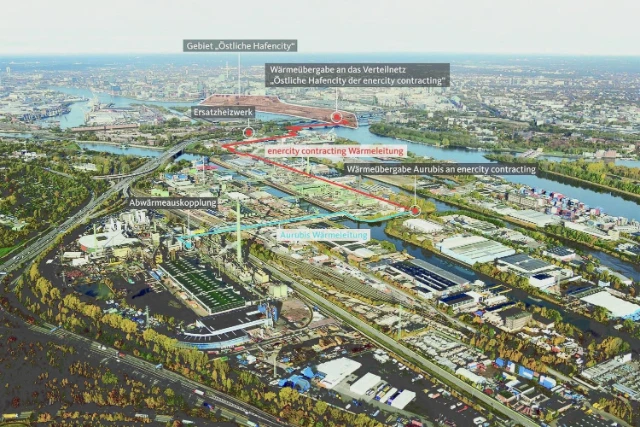
Technical modifications to the contact plant’s acid coolers in line 1. Increase in the temperature level to enable the extraction of industrial heat and construction of an industrial heat pipeline extending to the plant boundary to supply the neighborhood HafenCity East with heat. Preventing the discharge of 12 million m³ of cooling water into the Elbe River annually. Investments of roughly € 22 million.
Replacement of old wet gas cleaning in the concentrate drying drum of the primary smelter RWO by a modern dry filter installation • Reduction in accident risk due to improved ergonomics • 75 % reduction in dust emissions • 85 % reduction in SO2 emissions
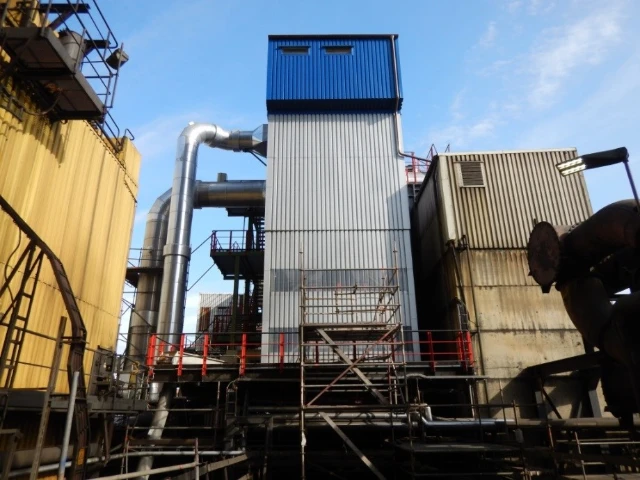
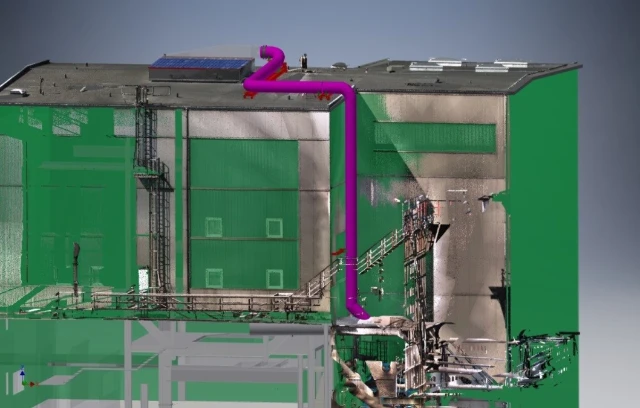


Installation of a 60,000 m³/h suctioning system on the secondary smelter’s e-furnace building. Filtering of exhaust air via existing filter.
Commissioning of a steam turbine to generate electricity. The previously unused pressure stage between 60 and 20 bar is made usable with the help of a superheater. This reduces about 5,000 t of CO2 per year.
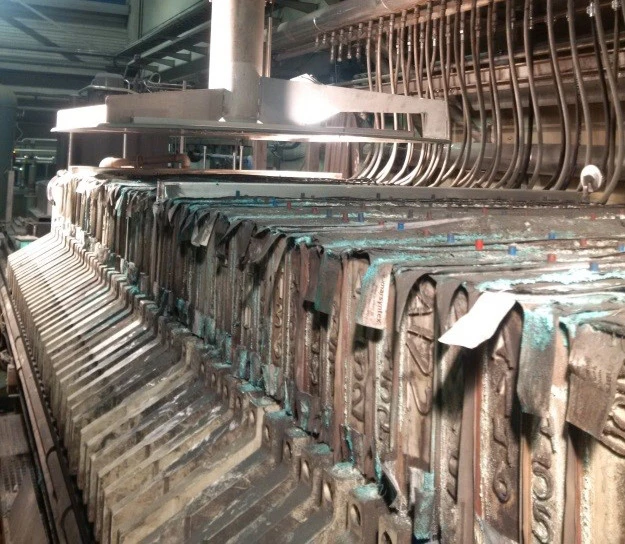

Commissioning of a modern, steam-heated anode slime press including a sliding off-gas hood to collect all of the thermally induced emissions above the press.
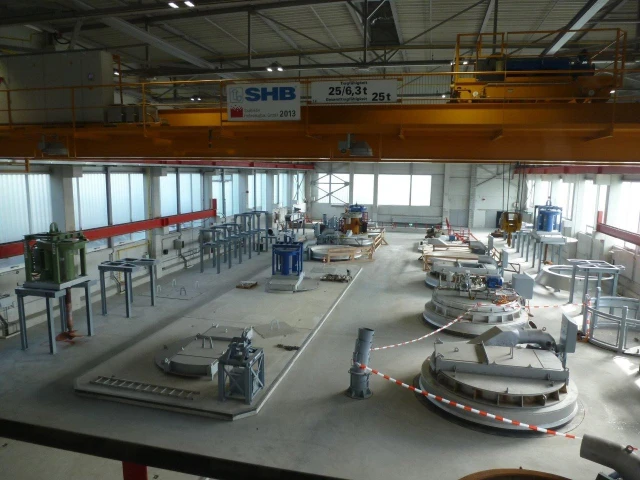

Replacement of the old lead refinery. Approx. 50 % reduction in fugitive emissions due to improved processes with a ventilation concept. Construction costs of roughly € 20 million.
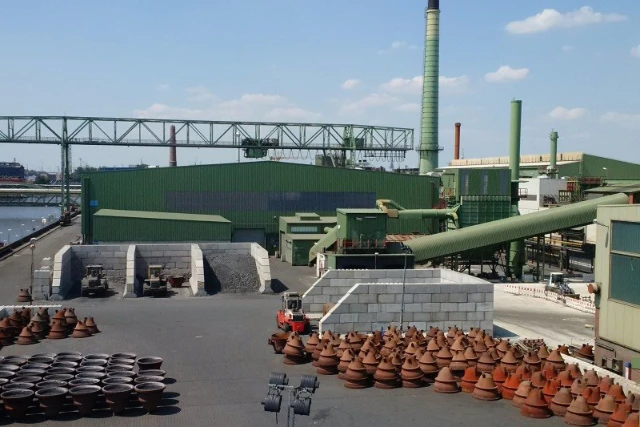

Construction of a storage hall including an enclosed, suctioned crusher for pollutant-laden bulk material in Plant North. Material is now transported via a fully closed system.
Construction of a new filter installation to continue reducing fugitive emissions in the converter area.
Commissioning of two washing towers to remove fluorides and other water-soluble components from the off-gas. The gas flows through the towers from below in a countercurrent to the washing water.

New off-gas collection system for anode furnace and casting machine reduces emissions in the area by more than 70 %. Investment of more than € 7 million.
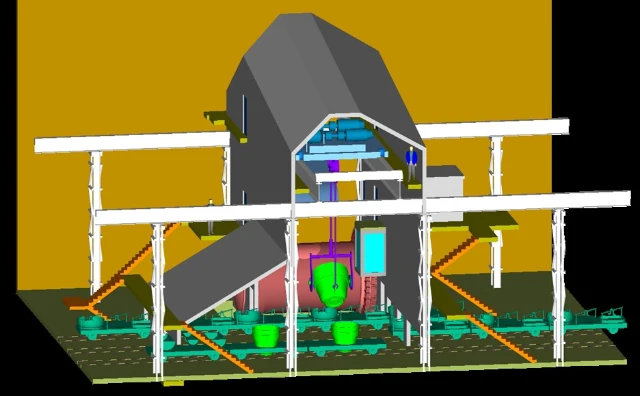
Enclosure and suctioning of Peirce-Smith converter in the Plant North primary smelter to collect and treat SO2-bearing off-gases from charging processes within the converter hall (house-in-house concept).
Certificates Aurubis Hamburg
-
Um die heruntergeladene Komponente zu sehen den QR code scannen
ISO 9001: 2015
PDF
1 MB
-
Um die heruntergeladene Komponente zu sehen den QR code scannen
DIN EN ISO 9001 : 2015, Annex
PDF
1 MB
-
Um die heruntergeladene Komponente zu sehen den QR code scannen
ISO 14001: 2015
PDF
1 MB
-
Um die heruntergeladene Komponente zu sehen den QR code scannen
DIN EN ISO 14001 : 2015, Annex
PDF
1 MB
-
Um die heruntergeladene Komponente zu sehen den QR code scannen
ISO 45001: 2018
PDF
1 MB
-
Um die heruntergeladene Komponente zu sehen den QR code scannen
DIN EN ISO 45001: 2018 Annex
PDF
1 MB
-
Um die heruntergeladene Komponente zu sehen den QR code scannen
ISO 50001: 2018
PDF
1 MB
Information to the public in accordance with the Major Accidents Ordinance
Arne Schilling
Head of Environmental Protection, Energy and Occupational Safety Hamburg, Plant Water Pollution Control Officer
| Phone | +49 40 7883-3788 |